2.1 大语言模型介绍 大语言模型的概念 大语言模型(英文:Large Language Model,缩写LLM), 也称大型语言模型,是一种人工智能模型,旨在理解和生成人类语言。
通常,大语言模型 (LLM) 指包含数十亿 (Billion 或更多)参数的语言模型,这些模型在大量的文本数据上进行训练,例如国外的有GPT-3 、GPT-4、PaLM 、Galactica 和 LLaMA 等,国内的有ChatGLM、文心一言、通义千问、讯飞星火等。
大模型的能力和特点
大模型的能力
大语言模型(LLM)与以前的预训练语言模型(PLM)的主要区别在于其涌现能力。这种能力在小型模型中不明显,但在大型模型中显著。例如:
上下文学习 :首次由GPT-3引入,允许模型在提供自然语言指令或多个任务示例的情况下,通过理解上下文并生成相应输出来执行任务。
指令遵循 :通过指令微调,LLM可以根据任务指令执行未见过的任务,展示出强大的泛化能力。
逐步推理 :通过”思维链(Chain of Thought, CoT) “策略,LLM能够解决多步推理任务,例如数学问题。
大模型的特点
巨大的规模 :参数规模达数十亿甚至数千亿,使其能捕捉更多语言知识和复杂语法结构。
预训练和微调 :在大规模无标签文本数据上预训练,然后通过有标签数据微调,适应特定任务。
上下文感知 :具备强大的上下文感知能力,能够理解和生成依赖前文的文本内容。
多语言支持 :支持多种语言,促进跨文化和跨语言的应用。
多模态支持 :一些LLM支持文本、图像和语音的多模态数据。
涌现能力 :在大规模模型中表现出明显的性能提升,能处理更复杂的任务。
多领域应用 :广泛应用于文本生成、自动翻译、信息检索、摘要生成、聊天机器人等多个领域。
伦理和风险问题 :需要谨慎处理生成有害内容、隐私问题和认知偏差等伦理和风险问题。
2.2 微调介绍 *什么是模型 微调
相当于给你一个预训练模型(Pre-trained model),基于这个模型微调(Fine Tune)。
预训练模型就是 已经用数据集训练好了的模型。
两种 Finetune 范式
增量预训练微调 (Continue PreTraining
使用场景:让基座模型学习到一些新知识,如某个垂类领域的常识
训练数据:文章、书籍、代码等
*指令跟随微调 (Supervised Finetuning )
使用场景:让模型学会对话模板,根据人类指令进行对话
训练数据:高质量的对话、问答数据
为什么要微调? 相对于从头开始训练(Training a model from scatch),微调可以省去大量计算资源和计算时间,提高了计算效率,甚至提高准确率。
普通预训练模型 的特点是:用了大型数据集做训练,已经具备了提取浅层基础特征和深层抽象特征的能力。
不做微调 :
(1)从头开始训练,需要大量的数据,计算时间和计算资源。
(2)存在模型不收敛,参数不够优化,准确率低,模型泛化能力低,容易过拟合等风险。
使用微调 :避免了上述可能存在的问题。
什么情况下使用微调? (1) 你要使用的数据集和预训练模型的数据集相似
如果不太相似,效果可能就没有那么好了,特征提取是不同的,所以相应的参数训练后也是不同的。
(2) 自己搭建或者使用的模型正确率太低。
(3)数据集相似,但数据集数量太少。
(4)计算资源太少。
不同数据集下使用微调
数据集1 - 数据量少,但数据相似度非常高在这种情况下,我们所做的只是修改最后几层或最终的softmax图层的输出类别。
数据集2 - 数据量少,数据相似度低在这种情况下,我们可以冻结预训练模型的初始层(比如k层),并再次训练剩余的(n-k)层。由于新数据集的相似度较低,因此根据新数据集对较高层进行重新训练具有重要意义。
数据集3 - 数据量大,数据相似度低在这种情况下,由于我们有一个大的数据集,我们的神经网络训练将会很有效。但是,由于我们的数据与用于训练我们的预训练模型的数据相比有很大不同。使用预训练模型进行的预测不会有效。因此,最好根据你的数据从头开始训练神经网络(Training from scatch)。
数据集4 - 数据量大,数据相似度高这是理想情况。在这种情况下,预训练模型应该是最有效的。使用模型的最好方法是保留模型的体系结构和模型的初始权重。然后,我们可以使用在预先训练的模型中的权重来重新训练该模型。
微调指导事项 1.通常的做法是截断预先训练好的网络的最后一层(softmax层),并用与我们自己的问题相关的新的softmax层替换它。例如,ImageNet上预先训练好的网络带有1000个类别的softmax图层。如果我们的任务是对10个类别的分类,则网络的新softmax层将由10个类别组成,而不是1000个类别。然后,我们在网络上运行预先训练的权重。确保执行交叉验证,以便网络能够很好地推广。 2.使用较小的学习率来训练网络。由于我们预计预先训练的权重相对于随机初始化的权重已经相当不错,我们不想过快地扭曲它们太多。通常的做法是使初始学习率比用于从头开始训练(Training from scratch)的初始学习率小10倍。 3. 如果数据集数量过少,我们进来只训练最后一层,如果数据集数量中等,冻结预训练网络的前几层的权重也是一种常见做法。
这是因为前几个图层捕捉了与我们的新问题相关的通用特征,如曲线和边。我们希望保持这些权重不变。相反,我们会让网络专注于学习后续深层中特定于数据集的特征。
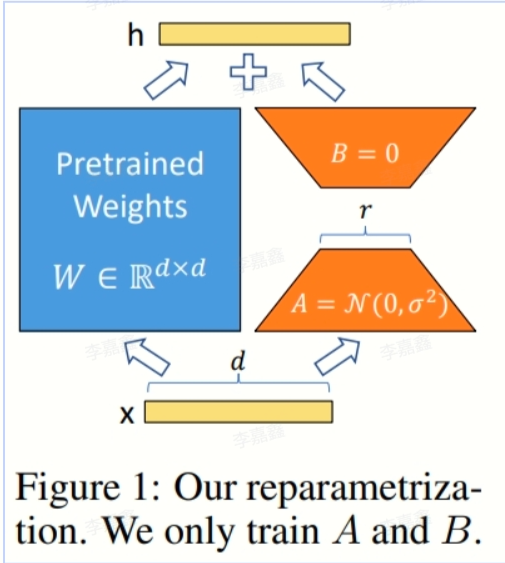
LoRA LoRA是一种高效微调方法,深入了解其原理可参见博客:[知乎|深入浅出Lora
LoRA 的优势
可以针对不同的下游任务构建小型 LoRA 模块,从而在共享预训练模型参数基础上有效地切换下游任务。
LoRA 使用自适应优化器(Adaptive Optimizer),不需要计算梯度或维护大多数参数的优化器状态,训练更有效、硬件门槛更低。
LoRA 使用简单的线性设计,在部署时将可训练矩阵与冻结权重合并,不存在推理延迟。
LoRA 与其他方法正交,可以组合。
LoRA 的原理
3.1 环境准备 相关库的下载与安装:
1 !pip install pandas openpyxl
数据加载与抽取
3.2 语文数据处理 3.2.1 数据加载 这里我们使用pandas加载xlsx中的数据,这里面我们使用全局匹配,将训练集中的中文点与左侧括号匹配为英文类型。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import pandas as pdimport redf = pd.read_excel('训练集-语文.xlsx' ) df = df.replace('.' , '.' , regex=True ) df = df.replace('(' , '(' , regex=True ) second_row_option_content = df.loc[2 , '选项' ] print (second_row_option_content)
3.2.2 抽取问题 这里主要是为了抽取题目及答案,并且过滤简答题。大家可以阅读详细的注释理解问题抽取的函数如何工作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 def chinese_multiple_choice_questions (questions_with_answers ): text = questions_with_answers question_pattern = re.compile (r'\d+\..*?(?=\d+\.|$)' , re.DOTALL) choice_pattern = re.compile (r'([A-D])\s*(.*?)(?=[A-D]|$|\n)' , re.DOTALL) questions = question_pattern.findall(text) multiple_choice_questions = [] short_answer_questions = [] for id ,question in enumerate (questions): if re.search(r'[A-D]' , question): choices = choice_pattern.findall(question) question_text = re.split(r'\n' , question.split('(' )[0 ])[0 ] pattern_question = re.compile (r'(\d+)\.(.*)' ) matches_question = str (id +1 )+'.' + pattern_question.findall(question_text)[0 ][1 ] multiple_choice_questions.append({ 'question' : matches_question, 'choices' : choices }) else : short_answer_questions.append(question.strip()) return multiple_choice_questions
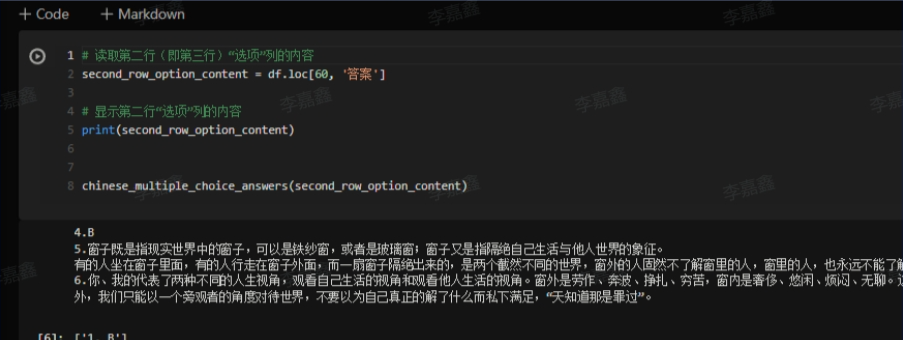
3.2.3 抽取问题的结果 这里我们抽取刚才我们拿到的选择题的答案部分。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 def chinese_multiple_choice_answers (questions_with_answers ): questions_with_answers = questions_with_answers.replace(" " , "" ).replace("\n" , "" ) choice_pattern = re.compile (r'(\d+)\.([A-Z]+)' ) short_pattern = re.compile (r'(\d+)\.([^A-Z]+)' ) choice_matches = choice_pattern.findall(questions_with_answers) short_matches = short_pattern.findall(questions_with_answers) choice_answers = {int (index): answer for index, answer in choice_matches} short_answers = {int (index): answer for index, answer in short_matches} sorted_choice_answers = sorted (choice_answers.items()) sorted_short_answers = sorted (short_answers.items()) answers = [] for id in range (len (sorted_choice_answers)): answers.append(f"{id +1 } . {sorted_choice_answers[id ][1 ]} " ) return answers
这里是一个样例~
3.2.4 prompt设计 正如我们1.4介绍的,我们使用要求+阅读材料组成prompt,作为input部分。
我们看看代码如何实现?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 def get_prompt_cn (text ): prompt = f''' 你是⼀个⾼考选择题出题专家,你出的题有⼀定深度,你将根据阅读文本,出4道单项选择题,包含题目选项,以及对应的答案,注意:不⽤给出原文,每道题由1个问题和4个选项组成,仅存在1个正确答案,请严格按照要求执行。 阅读文本主要是中文,你出的题目需要满足以下要点,紧扣文章内容且题干和答案为中文: ### 回答要求 (1)理解文中重要概念的含义 (2)理解文中重要句子的含意 (3)分析论点、论据和论证方法 ### 阅读文本 {text} ''' return prompt
可以看到代码里面首先对大模型做了声明,声明如下:
你是⼀个⾼考选择题出题专家,你出的题有⼀定深度,你将根据阅读文本,出4道单项选择题,包含题目选项,以及对应的答案,注意:不⽤给出原文,每道题由1个问题和4个选项组成,仅存在1个正确答案,请严格按照要求执行。 阅读文本主要是中文,你出的题目需要满足以下要点,紧扣文章内容且题干和答案为中文:
这里是官方的声明,不建议修改~
接下来是要求部分:(这里建议大家根据出题要求做修改尝试~)
### 回答要求
(1)理解文中重要概念的含义
(2)理解文中重要句子的含意
(3)分析论点、论据和论证方法
最后是阅读材料,这里其实是我们传入的阅读材料参数。
### 阅读文本
{text}
3.2.5 中文数据处理主函数 这段代码将input与output部分进行组合,按照列表序号一一对应~
可以看看注释中的实现细节~
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 def process_cn (df ): res_input = [] res_output = [] for id in range (len (df)): data_options = df.loc[id , '选项' ] data_answers = df.loc[id ,'答案' ] data_prompt = df.loc[id ,'阅读文本' ] data_options = chinese_multiple_choice_questions(data_options) data_answers = chinese_multiple_choice_answers(data_answers) data_prompt = get_prompt_cn(data_prompt) if (len (data_answers)==len (data_options)): res = '' for id_,question in enumerate (data_options): res += f''' {question['question' ]} ? ''' +'\n' for choise in question['choices' ]: res = res+ choise[0 ] + choise[1 ]+ '\n' res = res + '答案:' + str (data_answers[id_].split('.' )[-1 ]) + '\n' res_output.append(res) res_input.append(data_prompt) return res_input,res_output
3.3 英文数据处理 3.3.1 数据加载 和中文一样。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import pandas as pddf = pd.read_excel('训练集-英语.xlsx' ) df = df.replace('.' , '.' , regex=True ).replace('А.' , 'A.' , regex=True ).replace('В.' , 'B.' , regex=True ).replace('С.' , 'C.' , regex=True ).replace('D.' , 'D.' , regex=True ) second_row_option_content = df.loc[0 , '选项' ] print (second_row_option_content)
3.3.2 抽取问题 英文问题数据相对标准,但是也有不少小问题。比如ABCD的顺序可能是ACBD。我们看看这些如何解决。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 import retext = second_row_option_content def get_questions (text ): text = text.replace('\n' , ' ' )+' ' pattern = re.compile (r'(\d+\..*?)(A\..*?\s{2})([B-D]\..*?\s{2})([B-D]\..*?\s{2})(D\..*?\s{2})' , re.DOTALL) matches = pattern.findall(text) questions_dict_list = [] for match in matches: question, option1, option2, option3, option4 = match pattern_question = re.compile (r'(\d+)\.(.*)' ) question_text = pattern_question.findall(question.strip())[0 ][1 ] options = {option1[0 ]: option1, option2[0 ]: option2, option3[0 ]: option3, option4[0 ]: option4} question_dict = { 'question' : question_text, 'options' : { 'A' : options.get('A' , '' ).strip(), 'B' : options.get('B' , '' ).strip(), 'C' : options.get('C' , '' ).strip(), 'D' : options.get('D' , '' ).strip() } } questions_dict_list.append(question_dict) return questions_dict_list questions = get_questions(text) for q in questions: print (q)
3.3.3 抽取问题的结果 1 2 3 4 5 def remove_whitespace_and_newlines (input_string ): result = input_string.replace(" " , "" ).replace("\n" , "" ).replace("." , "" ) return result
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import retext = """ 32. B. The underlying logic of the effect. 33.D. estimates were not fully independent. 34.C. The discussion process. 35.D. Approving. """ def get_answers (text ): text = remove_whitespace_and_newlines(text) pattern = re.compile (r'(\d)\s*([A-D])' ) matches = pattern.findall(text) res = [] for match in matches: number_dot, first_letter = match res.append(first_letter) return res
3.3.4 prompt设计 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 def get_prompt_en (text ): prompt = f''' 你是⼀个⾼考选择题出题专家,你出的题有⼀定深度,你将根据阅读文本,出4道单项选择题,包含题目选项,以及对应的答案,注意:不⽤给出原文,每道题由1个问题和4个选项组成,仅存在1个正确答案,请严格按照要求执行。 The reading text is mainly in English. The questions and answers you raised need to be completed in English for at least the following points: ### 回答要求 (1)Understanding the main idea of the main idea. (2)Understand the specific information in the text. (3)infering the meaning of words and phrases from the context ### 阅读文本 {text} ''' return prompt
可以看到代码里面首先对大模型做了声明,声明如下:
你是⼀个⾼考选择题出题专家,你出的题有⼀定深度,你将根据阅读文本,出4道单项选择题,包含题目选项,以及对应的答案,注意:不⽤给出原文,每道题由1个问题和4个选项组成,仅存在1个正确答案,请严格按照要求执行。
The reading text is mainly in English. The questions and answers you raised need to be completed in English for at least the following points:
这里是官方的声明,不建议修改~
接下来是要求部分:(这里建议大家根据出题要求做修改尝试~)
### 回答要求
(1)Understanding the main idea of the main idea.
(2)Understand the specific information in the text.
(3)infering the meaning of words and phrases from the context
最后是阅读材料,这里其实是我们传入的阅读材料参数。
### 阅读文本
{text}
3.3.5 英文数据处理主函数 这里大家可以参考中文部分对比学习,相比中文简单很多~
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 def process_en (df ): res_input = [] res_output = [] for id in range (len (df)): data_options = df.loc[id , '选项' ] data_answers = df.loc[id ,'答案' ] data_prompt = df.loc[id ,'阅读文本' ] data_options = get_questions(data_options) data_answers = get_answers(data_answers) data_prompt = get_prompt_en(data_prompt) if (len (data_answers)==len (data_options)): res = '' for id ,question in enumerate (data_options): res += f''' {id +1 } .{question['question' ]} {question['options' ]['A' ]} {question['options' ]['B' ]} {question['options' ]['C' ]} {question['options' ]['D' ]} answer:{data_answers[id ]} ''' +'\n' res_output.append(res) res_input.append(data_prompt) return res_input,res_output
3.4 数据合并 因为微调需要150条数据,数据处理后得到有效数据为102,从中文抽取30条,英文抽取20条组成152条数据作为微调数据。
1 2 3 df_new = pd.DataFrame({'input' : cn_input+cn_input[:30 ]+en_input+en_input[:20 ], 'output' : cn_output+cn_output[:30 ]+en_output+en_output[:20 ]})